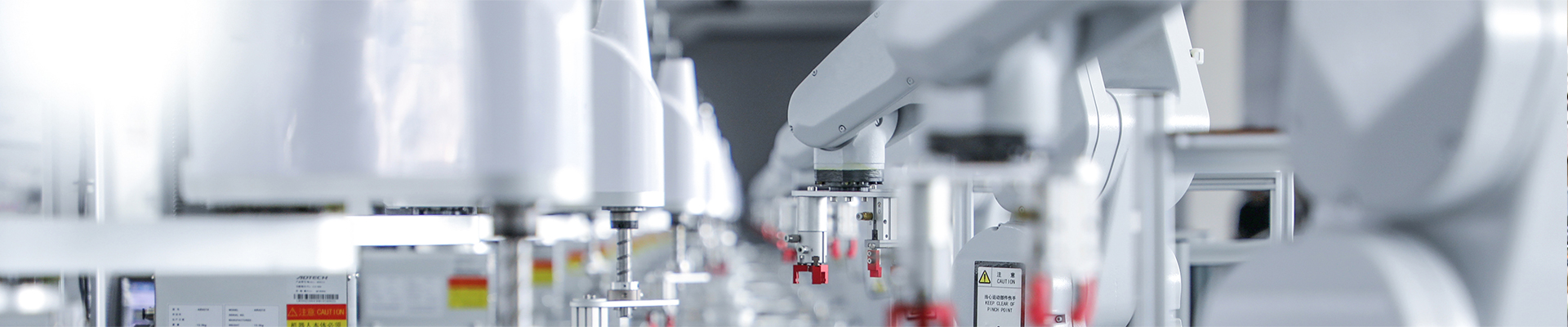
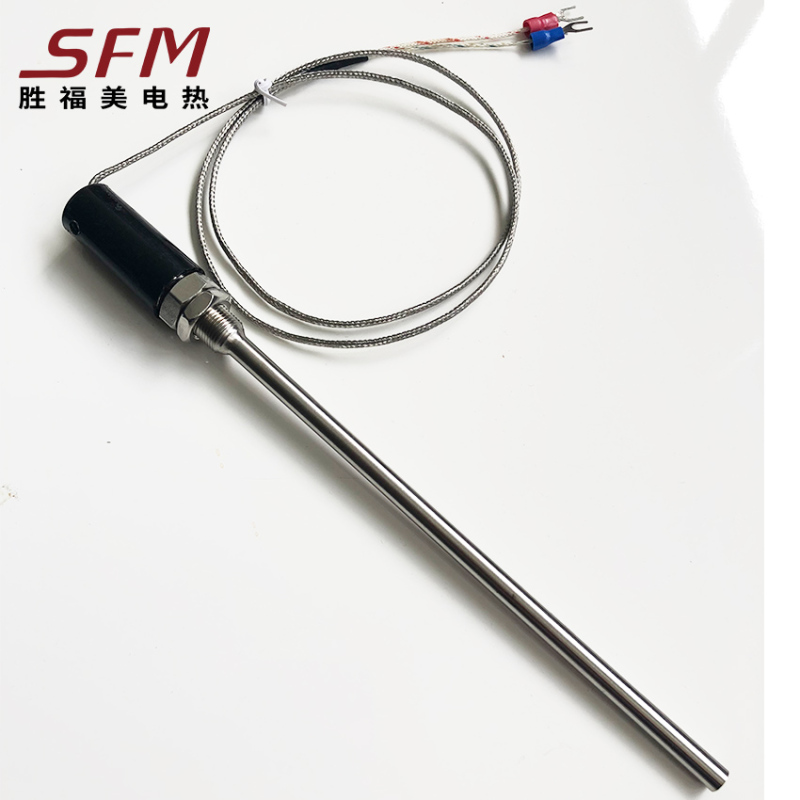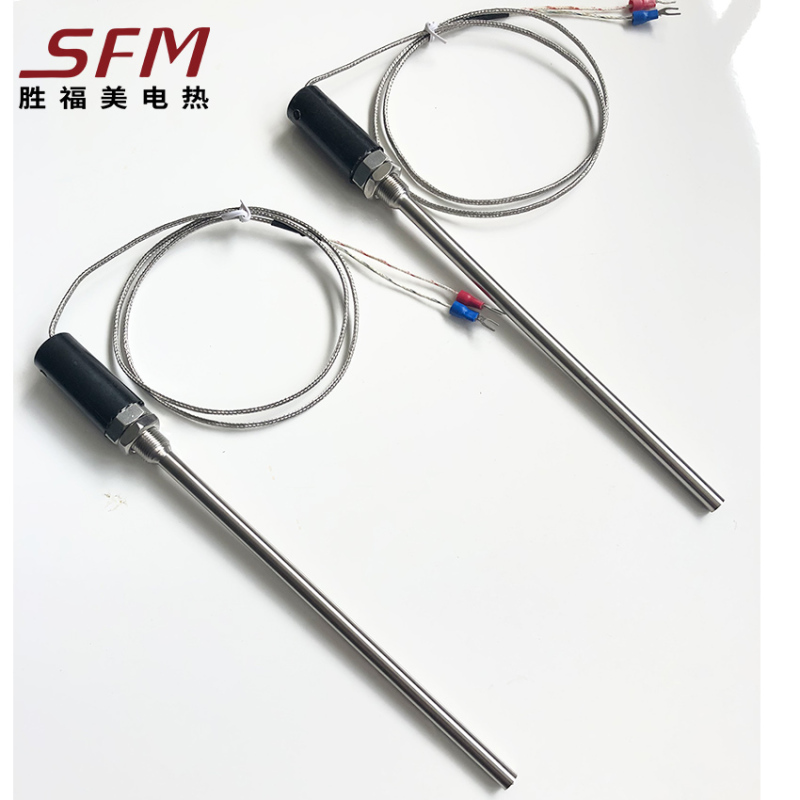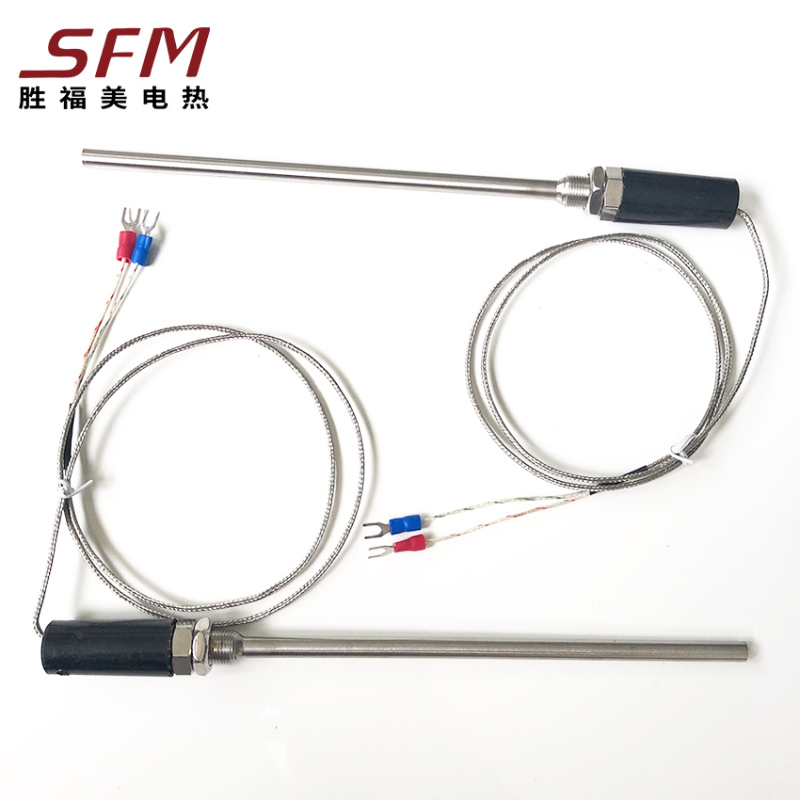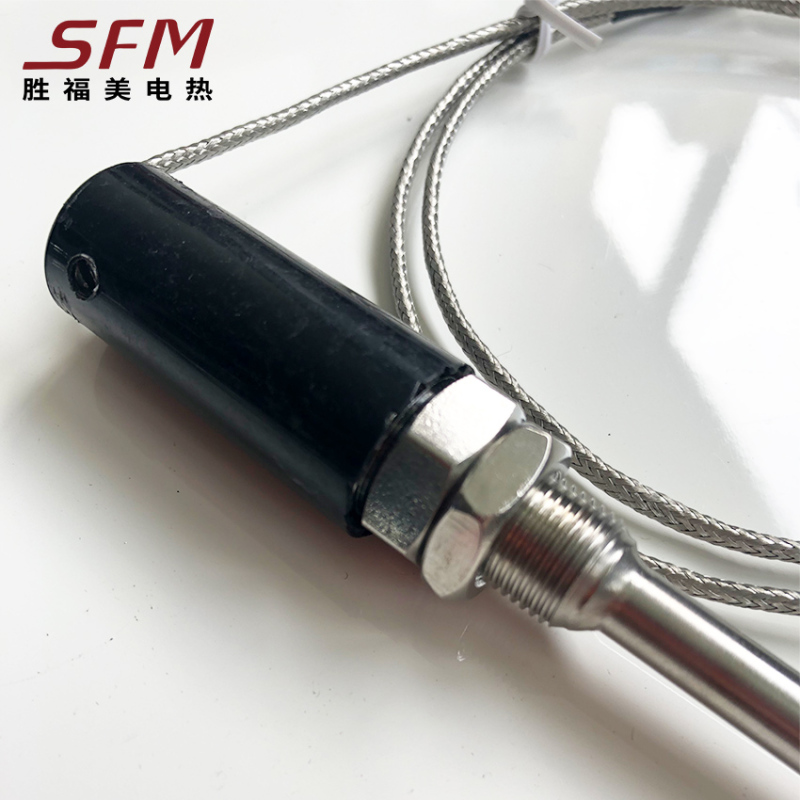
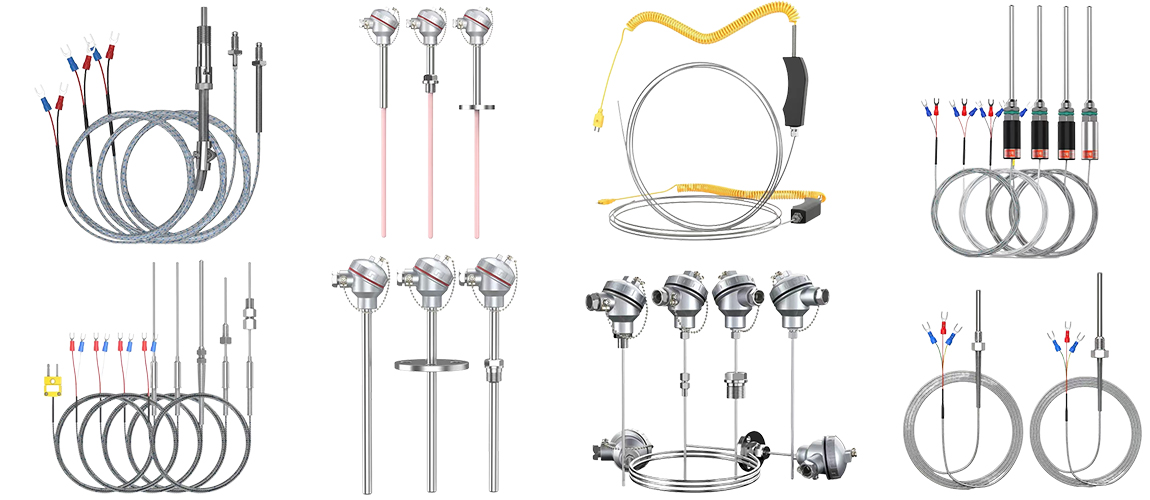
J Type Compression Spring Thermocouple
thermocouple as measure temperature sensor, and usually display meter, recording meter and
electronic regulator, at the same time, also can be used as a prefabricated thermocouple temperature
sensing element, it can be directly measured from 0 ℃ ~ 800 ℃ in the process of various production
within the scope of the liquid, steam and gas medium, as well as the temperature of the solid surface
- SFM
- china
- 2-7 day
- Information
SHEATH MATERIAL
SUS304
SUS316 - Excellent pitting corrosion resistance & crevice corrosion resistance, widely used in the chemical industry.
Inconel600 - Heat & corrosion resistant steel with strong stress and corrosion resistance, widely used in various heating components and petrochemical industry.
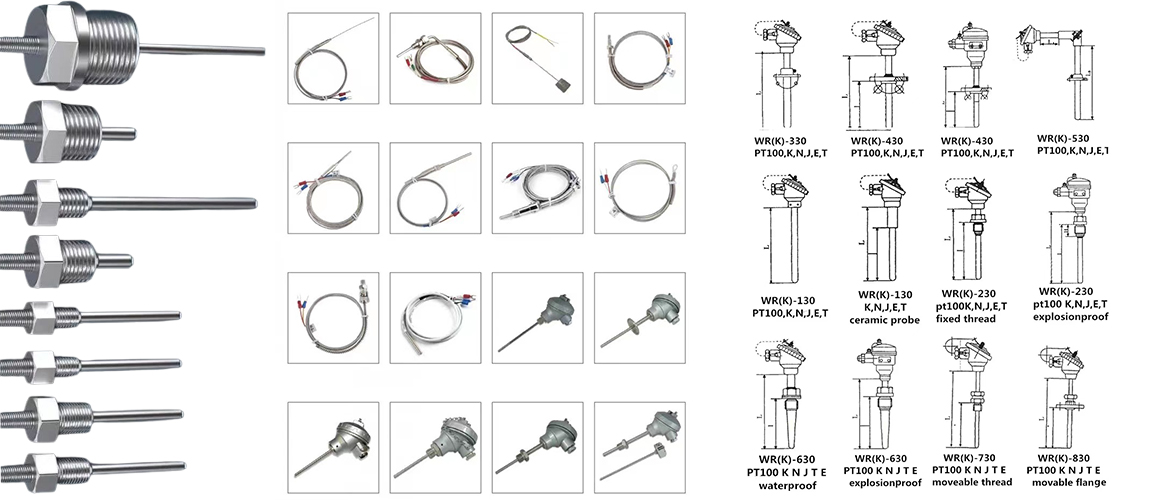
MOUNTING & FIXING
A variety of mounting options including fixed or movable flange, fixed or movable thread, or without mounting fixing.
JUNCTION STYLES & DETAILS
Grounded
1. Good heat transfer from the outside to the thermocouple junction
2. Rapid response
3. No suitable in case with electrical noise
Ungrounded
1. Response time is slower than the grounded style
2. Long service life
3. Resistance to electrical noise
Exposed
1. Rapid response
2. Suitable to measure the temperature of gas
3. Poor mechanical strength in contact with other measuring structures

Thermocouple Types and Temperature Range
| ||||
Type | Wire Material | Temp. Range | Accuracy | |
+ | - | |||
K | Nickel-Chromium | Nickel-Alumel | -200~1000°C | +/- 2.2°C or +/- .75% |
J | Iron | Constantan | 0~600°C | +/- 2.2°C or +/- .75% |
T | Copper | Constantan | -200~300°C | +/- 1.0°C or +/- .75% |
E | Nickel-Chromium | Constantan | -200~700°C | +/- 1.7°C or +/- 0.5% |
N | Nicrosil | Nisil | -200~1200°C | +/- 2.2°C or +/- .75% |
R | Platinum Rhodium – 13% | Platinum | 0~1400°C | +/- 1.5°C or +/- .25% |
S | Platinum Rhodium – 10% | Platinum | 0~1400°C | +/- 1.5°C or +/- .25% |
B | Platinum Rhodium – 30% | Platinum Rhodium – 6% | 0~1500°C | +/- 0.5% |

Thermocouple Type | Extension Wire Type | Wire Material | Temp. Range (℃) | Tolerance (µV) | ||
+ | - | Class 1 | Class 2 | |||
K | KX | Nickel-chrome | Nickel-silicon | -25~200 | ±60 | ±100 |
KCA | Nickel-chrome | Nickel-silicon | 0~150 | - | ±100 | |
KCB | Iron | Copper-nickel | 0~150 | - | ±100 | |
KCC | Copper | Copper-nickel | 0~100 | - | ±100 | |
E | EX | Nickel-chrome | Copper-nickel | -25~200 | ±120 | ±200 |
J | JX | Iron | Copper-nickel | -25~200 | ±85 | ±140 |
T | TX | Copper | Copper-nickel | -25~100 | ±30 | ±60 |
N | NX | Nickel-chrome | Nickel-silicon | -25~200 | ±60 | ±100 |
NC | Copper-nickel | Copper-nickel | 0~150 | - | ±100 | |
R | RCA | Copper | Copper-nickel | 0~100 | - | ±30 |
RCB | Copper | Copper-nickel | 0~200 | - | ±60 | |
B | BC | Copper | Copper | 0~100 | - | - |
S | SCA | Copper | Copper-nickel | 0~100 | - | ±30 |
SCB | Copper | Copper-nickel | 0~200 | - | ±60 | |
Features | 1. Cost effective 2. Small in size 3. Robust 4. Wide range of operation 5. Accurate for large temperature changes 6. Fast response 7. Wide temperature capabilities |
How to choose | Please provide the following information: 1. What’s the application 2. Type of the thermocouple (K/J/T/E/N/R/S/B) 3. Diameter and length of probe 4. Installation requirements (thread or flange size) 5. Temperature range 6. Chemical resistance of the thermocouple or sheath material |















